Class 11 cell membrane-
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a fundamental structure that surrounds and encloses the contents of a cell, separating it from its external environment. It is a crucial component of all cells, providing a barrier that controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell. The cell membrane has several important functions:
- Selective Permeability: The membrane is selectively permeable, meaning it allows certain substances to pass through while preventing the entry or exit of others. This selective permeability is essential for maintaining the internal environment of the cell.
- Barrier Function: The cell membrane acts as a physical barrier, preventing the mixing of the cell’s internal components with the external environment. It helps to maintain the distinct identity of the cell.
- Transport: The membrane facilitates the transport of molecules in and out of the cell through various mechanisms, such as passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport.
- Cell Recognition: Cell membranes often have proteins and carbohydrates on their surface that play a role in cell recognition and communication. These molecules are involved in processes like cell signaling and immune responses.
- Cell Adhesion: The membrane helps cells adhere to each other and to the extracellular matrix, forming tissues and maintaining the structural integrity of multicellular organisms.
- Signal Transduction: Proteins embedded in the cell membrane can act as receptors, receiving signals from the external environment and transmitting them to the inside of the cell to initiate specific cellular responses.
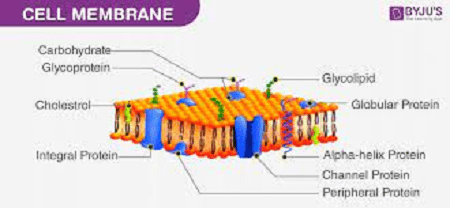
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a lipid bilayer, consisting of phospholipids arranged with their hydrophobic tails facing inward and their hydrophilic heads facing outward. Proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol are also embedded in the membrane, contributing to its structure and function.
Overall, the cell membrane is a dynamic and essential structure that plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and functionality of cells.
What is Required Class 11 cell membrane
In Class 11 biology, students typically study the cell membrane as part of the broader topic of “Cell: The Unit of Life.” The study of the cell membrane includes understanding its structure, functions, and various processes associated with it. Here’s a brief outline of what is usually covered regarding the cell membrane in Class 11:
- Cell Structure:
- Overview of cell structure, including the cell membrane.
- Distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Basic understanding of the cell as the structural and functional unit of life.
- Cell Membrane:
- Introduction to the cell membrane as the outermost boundary of the cell.
- Composition of the cell membrane, including lipids (phospholipids), proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane.
- Structure of the Cell Membrane:
- Explanation of the lipid bilayer and its hydrophilic and hydrophobic components.
- Roles of proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates in the structure and function of the membrane.
- Functions of the Cell Membrane:
- Selective permeability and its importance in maintaining cell homeostasis.
- Transport mechanisms, including passive and active transport.
- Cell adhesion, communication, and recognition functions.
- Transport Across Cell Membrane:
- Passive transport: Diffusion and osmosis.
- Active transport: Primary and secondary active transport.
- Cell Communication:
- Cell signaling and the role of membrane receptors.
- Signal transduction pathways.
- Cell Adhesion:
- Importance of cell adhesion in the formation of tissues and organs.
- Experimental Techniques:
- Techniques used to study the cell membrane, such as electron microscopy and freeze-fracture techniques.
It’s important to note that the specific content and depth of coverage may vary depending on the curriculum and educational board. Students are encouraged to refer to their textbooks and class notes for detailed information and to participate in practical demonstrations and laboratory exercises to reinforce their understanding of cell membrane concepts.
Who is Required Class 11 cell membrane
The term “cell membrane” refers to a biological structure rather than a person. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a fundamental component of cells in living organisms. It is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell, separating its internal environment from the external surroundings.
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a lipid bilayer, consisting of phospholipids arranged with their hydrophilic heads facing outward and hydrophobic tails facing inward. Proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol are also embedded in the membrane, contributing to its structure and functionality.
The main functions of the cell membrane include selective permeability, allowing certain substances to pass through while restricting others, maintaining the cell’s internal environment, facilitating various forms of cellular transport, and playing a role in cell signaling, adhesion, and recognition.
In summary, the cell membrane is a crucial and dynamic structure that plays a fundamental role in the biology of cells. It is not a person but a key component of cellular biology.
When is Required Class 11 cell membrane
If you are asking when the study of the cell membrane is typically covered in Class 11, it is usually part of the broader topic of “Cell: The Unit of Life” in the biology curriculum.
The study of the cell membrane, its structure, functions, and associated processes is an essential component of high school biology. It is often covered early in the academic year or semester, depending on the specific curriculum and educational system. The focus on the cell membrane helps students understand the basic building blocks of life and the fundamental principles of cell biology.
If you have a more specific question or if there was a misunderstanding in your inquiry, please provide additional details, and I’ll do my best to assist you.
Where is Required Class 11 cell membrane
If you are asking about the specific location or context in which the study of the cell membrane is addressed in Class 11, it typically falls within the broader subject of biology. In most educational systems, high school students, particularly in Class 11 or its equivalent, study biology as a subject.
The cell membrane is a fundamental topic in biology and is usually covered when students learn about the structure and function of cells. The study of the cell membrane is part of understanding the basic principles of cell biology and is often included in chapters or units related to cell structure, cellular processes, or cell biology in general.
If you have a more specific question or if there’s a particular aspect you’re curious about, please provide additional details so that I can offer more targeted assistance.
How is Required Class 11 cell membrane
It seems there might be a phrasing issue in your question, but if you’re asking about how the cell membrane is studied or taught in Class 11 (which is typically a grade or level in high school education), the cell membrane is introduced and explored through various approaches:
- Classroom Lectures: Teachers usually provide foundational information about the cell membrane, covering its structure, composition, and functions. This may include discussions on the fluid mosaic model, phospholipid bilayer, proteins, and their roles in selective permeability.
- Textbooks: Students often use biology textbooks that are specifically designed for the Class 11 curriculum. These books typically contain detailed explanations, diagrams, and examples related to the cell membrane.
- Laboratory Work: In some cases, students may engage in laboratory activities to observe and experiment with cell membranes. This could involve experiments related to osmosis, diffusion, or the use of microscopy to visualize cell structures.
- Visual Aids: Teachers may use visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and animations to help students better understand the structure and functions of the cell membrane.
- Interactive Learning: Some educational systems incorporate interactive learning tools, simulations, or online resources to enhance students’ understanding of the cell membrane.
- Assessments: Students are often evaluated through exams, quizzes, or assignments to ensure they have grasped the concepts related to the cell membrane.
The goal is to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the cell membrane’s importance, structure, and functions, laying the foundation for more advanced biological concepts in subsequent classes. If you have a more specific question or if there’s a particular aspect you’d like more information on, please feel free to clarify!
Case study on Class 11 cell membrane
While I cannot provide a specific case study, I can outline a hypothetical scenario for a case study on the cell membrane that could be suitable for a Class 11 biology class. Keep in mind that case studies are often designed to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving, applying their knowledge of the cell membrane in a real-world context. Here’s an example:
Case Study: The Mystery of Cell Membrane Dysfunction
Background: A small community is experiencing an unusual health issue among its residents. Several individuals have reported symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and difficulty concentrating. The local health authorities are investigating a possible link between these health concerns and exposure to a particular environment.
Scenario:
- Patient Profiles:
- Identify individuals experiencing health issues and gather information on their lifestyles, activities, and environments.
- Explore any commonalities among affected individuals.
- Research:
- Investigate the environmental factors in the community, such as pollution, chemical exposure, or changes in water sources.
- Explore the possibility of a link between the symptoms and the cell membrane’s function.
- Laboratory Analysis:
- Conduct laboratory tests on affected individuals to examine their cell membranes.
- Explore the lipid composition, protein structure, and functionality of the cell membranes.
- Cell Membrane Function:
- Connect the symptoms to potential disruptions in cell membrane functions.
- Investigate how changes in the cell membrane might affect nutrient transport, signaling, or other essential processes.
- Treatment Options:
- Propose potential treatment options based on addressing cell membrane dysfunction.
- Explore lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, or medications that could restore normal cell membrane function.
- Public Health Recommendations:
- Develop recommendations for the community to mitigate exposure to potential factors affecting cell membrane health.
- Educate residents on the importance of maintaining a healthy cell membrane.
Discussion Points:
- How do changes in the cell membrane impact overall cell function?
- What are the potential causes of cell membrane dysfunction in this scenario?
- How can understanding cell membrane structure and function guide treatment strategies?
- What preventive measures can be recommended at the individual and community levels?
This case study encourages students to integrate their knowledge of the cell membrane with critical thinking skills to analyze a real-world health issue. It also emphasizes the interdisciplinary nature of biology, considering environmental factors, health outcomes, and potential interventions.
White paper on Class 11 cell membrane
Creating a comprehensive white paper on the Class 11 cell membrane involves an in-depth exploration of its structure, functions, and significance in biology education. Below is an outline for a white paper on the cell membrane in the context of Class 11 biology:
Title: Understanding the Cell Membrane: A Comprehensive Overview for Class 11 Biology Education
Executive Summary:
Provide a brief overview of the importance of studying the cell membrane in Class 11 biology. Highlight its role in cellular function, the relevance to broader biological concepts, and its significance in real-world applications.
1. Introduction:
- Background:
- Brief history of cell membrane discovery.
- Importance of the cell membrane in cell biology.
- Relevance to Class 11:
- Position the cell membrane within the Class 11 biology curriculum.
- Outline its role in laying the foundation for advanced biological concepts.
2. Structure of the Cell Membrane:
- Lipid Bilayer:
- Overview of the lipid bilayer and its composition.
- Explanation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions.
- Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Cholesterol:
- Role of proteins in membrane structure and function.
- Significance of carbohydrates in cell communication.
- Contribution of cholesterol to membrane stability.
3. Functions of the Cell Membrane:
- Selective Permeability:
- Explanation of how the membrane selectively allows substances to pass through.
- Importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
- Transport Mechanisms:
- Passive transport (diffusion, osmosis).
- Active transport (primary and secondary active transport).
- Cell Communication:
- Overview of membrane receptors and signal transduction pathways.
4. Classroom Approaches and Teaching Strategies:
- Lectures and Discussions:
- Effective ways to convey complex membrane concepts.
- Incorporating real-world examples to enhance understanding.
- Laboratory Experiments:
- Practical experiments to visualize and understand membrane properties.
- Demonstrations related to diffusion, osmosis, and transport.
- Interactive Learning Tools:
- Utilizing technology for interactive simulations.
- Online resources for self-directed learning.
5. Case Studies:
- Real-World Applications:
- Integration of cell membrane concepts into case studies.
- Examples linking cell membrane dysfunction to health issues.
6. Future Directions and Advances:
- Current Research:
- Overview of recent studies related to cell membrane research.
- Emerging technologies and their impact on our understanding.
7. Conclusion:
- Summary:
- Recapitulation of key points.
- Emphasis on the importance of the cell membrane in biological education.
8. References:
Provide a comprehensive list of references, including textbooks, research papers, and online resources that educators and students can explore for further study.
This white paper serves as a resource for educators, students, and researchers interested in a detailed exploration of the cell membrane within the context of Class 11 biology education. It aims to provide both theoretical knowledge and practical approaches to enhance the learning experience surrounding this fundamental biological concept.
Industrial application of Class 11 cell membrane
While Class 11 biology typically focuses on the fundamental concepts of the cell membrane, it’s interesting to explore how the understanding of cell membrane functions can have applications in various industries. Here are some industrial applications related to cell membranes:
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Drug Development: Understanding cell membrane structure and function is crucial in drug development. Researchers study how substances interact with cell membranes to design more effective and targeted pharmaceuticals.
- Bioprocessing: In the production of biopharmaceuticals, cell membranes are considered in cell culture processes to optimize growth conditions and enhance product yield.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
- Food Preservation: Knowledge of cell membrane properties is relevant in food preservation techniques. For example, understanding osmotic pressure helps in developing strategies for preserving fruits and vegetables.
- Flavor Release: Understanding how flavor compounds interact with cell membranes can be essential in the development of enhanced or controlled-release flavors.
- Agriculture:
- Crop Protection: Pesticides and herbicides often target cell membranes of pests and unwanted plants. Knowledge of membrane properties aids in the development of effective and environmentally friendly agricultural chemicals.
- Environmental Science:
- Bioremediation: Understanding how microorganisms interact with cell membranes can be applied in bioremediation efforts to clean up environmental pollutants.
- Wastewater Treatment: Membrane filtration technologies are used in wastewater treatment processes to separate impurities from water.
- Energy Production:
- Biofuel Production: Understanding cellular transport mechanisms and membrane properties is relevant in the development of biofuel production processes using microorganisms.
- Fuel Cells: Research on the cell membrane aids in the development of fuel cell technologies where biological membranes are used for energy production.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care:
- Skin Penetration: Understanding how substances interact with cell membranes is crucial in the formulation of skincare products. This knowledge helps in designing products that penetrate the skin effectively.
- Materials Science:
- Nanotechnology: The study of cell membranes contributes to the development of biomimetic materials. Researchers use insights from cell membranes to design nanostructures with specific functions.
- Biomedical Engineering:
- Artificial Organs and Tissues: Knowledge of cell membranes is crucial in the development of artificial organs and tissues. Biomimetic membranes are used in creating functional devices for medical applications.
In each of these industries, a deeper understanding of cell membrane biology can lead to more efficient processes, improved product development, and the creation of innovative technologies. The interdisciplinary nature of cell membrane research makes it applicable in diverse industrial contexts.


